What Is Data Collection: Methods, Types, and Tools
Data collection is the foundation of informed decision-making in business, research, education, and many other fields. Whether it’s to understand customer behavior, evaluate project outcomes, or support scientific research, data collection allows us to transform raw information into actionable insights.
This article explains what data collection is, the different types and methods used, and the most effective tools for gathering data accurately.
What Is Data Collection
Data collection is the process of systematically gathering information from various sources to analyze and make decisions. This information can be numerical, descriptive, behavioral, or observational.
Organizations and researchers use data collection to evaluate hypotheses, track performance, understand user behavior, and drive growth through data-driven strategies.
Types of Data in Data Collectio
Understanding the nature of the data you want to collect is essential. There are two main types of data:
Qualitative Data
Qualitative data is descriptive and non-numerical. It explores the why and how of decision-making, experiences, and emotions.
Examples:
- Interview transcripts
- Customer feedback
- Social media comments
Quantitative Data
Quantitative data is measurable and numerical. It provides statistical insights and is used for comparing, analyzing, and predicting patterns.
Examples:
- Sales numbers
- Survey ratings
- Website visitor counts
Methods of Data Collection
There are various methods for collecting data. The choice depends on the type of data needed, the research goals, and available resources.
1. Surveys and Questionnaires
Surveys are a structured method for collecting quantitative or qualitative information from a target group. They can be conducted online, in-person, or via phone.
Use case: Market research, customer satisfaction, academic studies.
2. Interviews
Interviews are one-on-one discussions that provide deep, personalized insights into opinions, motivations, and behaviors. These are usually qualitative.
Use case: Employee feedback, case studies, user research.
3. Observations
Observation involves directly monitoring subjects in their environment without interference. This method is ideal for collecting behavioral data.
Use case: Usability testing, classroom assessments, ethnographic research.
4. Focus Groups
A focus group brings together a small, diverse group of people to discuss a topic. Researchers observe responses and group dynamics to extract insights.
Use case: Product development, advertising feedback.
5. Experiments
Experiments involve manipulating variables under controlled conditions to measure cause-effect relationships. This method is mostly quantitative.
Use case: A/B testing, scientific trials, behavioral studies.
6. Web and App Analytics
Digital platforms automatically collect user interaction data. These tools help track visitor behavior, session durations, conversion rates, and more.
Use case: Website optimization, digital marketing, product analytics.
Popular Tools for Data Collection
Here are some of the most widely used tools for collecting data effectively:
| Tool | Function | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Google Forms | Online surveys | Education, feedback collection |
| Typeform | Interactive forms | UX-focused surveys |
| SurveyMonkey | Professional surveys | Market research, enterprise surveys |
| Google Analytics | Web analytics | Tracking visitor behavior |
| Hotjar | User behavior tracking | Heatmaps, session recordings |
| Zoho Forms | Business forms | Customer data collection |
| Microsoft Excel / Google Sheets | Manual data entry | Simple data logging and analysis |
Each tool has its strengths. Choose based on your project goals, budget, and technical skills.
Why Is Data Collection Important?
Accurate data collection is critical for:
- Making informed, evidence-based decisions
- Understanding user or customer needs
- Measuring performance and outcomes
- Supporting innovation and product development
- Ensuring accountability and transparency
Poor data leads to poor decisions. That’s why data collection must be structured, ethical, and aligned with objectives.
Best Practices for Effective Data Collection
To ensure your data collection process delivers high-quality results, follow these best practices:
- Define clear objectives: Know what you want to achieve.
- Select the right method: Match the method to your data type and audience.
- Ensure data privacy: Comply with data protection laws like GDPR.
- Validate and clean data: Remove duplicates, errors, and outliers before analysis.
- Use standardized tools: Improve consistency and scalability.
Conclusion
Data collection is more than just gathering information—it’s the starting point for insights, strategy, and innovation. Whether you’re a business leader, academic researcher, or data analyst, mastering data collection techniques and tools is essential for long-term success.
Read also: Full Stack Developer Course in Bangalore
Choose the right methods, use the best tools, and always prioritize data quality and ethics. In the world of data, precision and planning make all the difference.
Q&A-Google’s People Also Ask
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is data collection?
Data collection is the process of systematically gathering and measuring information from various sources to answer research questions, test hypotheses, or support business decision-making. It is a foundational step in data analysis and research.
2. What are the types of data collection?
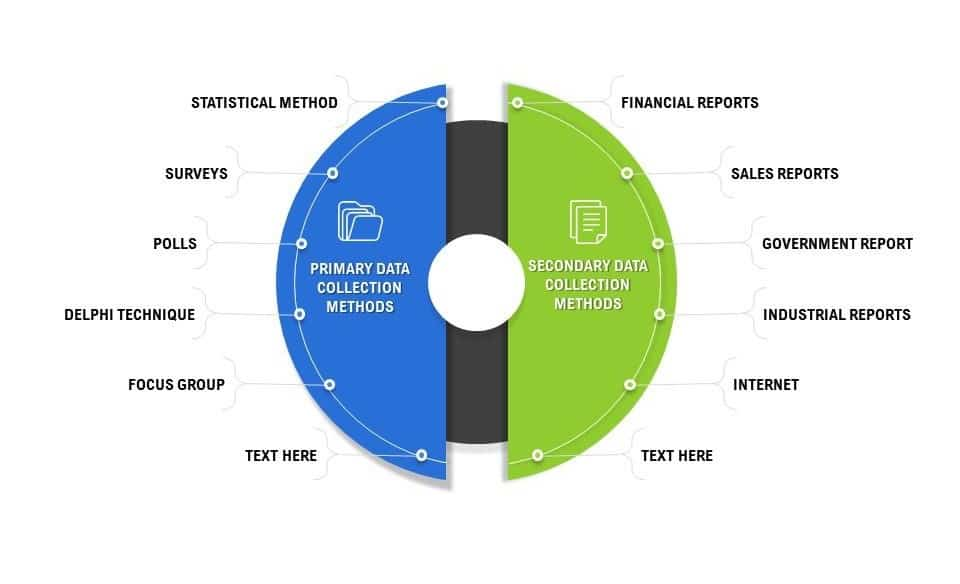
There are two main types of data collection:
- Primary data collection: Involves collecting data directly from original sources using methods like surveys, interviews, and observations.
- Secondary data collection: Involves using existing data from reports, databases, or published research.
Each type serves different purposes and is chosen based on the research objective.
3. What are common data collection methods?The most common data collection methods include:
- Surveys and questionnaires
- Interviews (structured or unstructured)
- Observations
- Focus groups
- Experiments
- Web and app analytics
The method you choose depends on whether you’re collecting qualitative or quantitative data.
4. What are the best data collection tools?Some of the best tools for collecting and analyzing data are:
- Google Forms: Free and easy-to-use for basic surveys
- SurveyMonkey: Ideal for professional-level data collection
- Typeform: Offers user-friendly, interactive forms
- Google Analytics: Best for tracking website visitor behavior
- Hotjar: Provides heatmaps and user behavior recordings
- Zoho Forms: Great for business forms and automation
Choose a tool based on your budget, complexity, and technical needs.
5. What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative data?
- Qualitative data is descriptive, non-numerical, and explores concepts or experiences (e.g., user feedback, interview answers).
- Quantitative data is numerical and can be measured or statistically analyzed (e.g., sales numbers, survey ratings).
Both types are essential, often used together for deeper insights.
6. Why is data collection important?
Data collection is important because it:
- Enables informed decision-making
- Supports accurate research findings
- Helps businesses understand customer behavior
- Improves operational efficiency
- Ensures accountability and transparency
Without accurate data, strategies and decisions become guesswork rather than evidence-based.
Read Also: Highest Paying Jobs in India 2025







